DIFFERENCE HEADSET IN SPEAKER DESIGN CHARACTERISTICS
2026-03-02
1. Lightweight Call Center Headsets
Core Objectives: Voice clarity, communication efficiency, and long‑term wearing comfort.
Speaker Characteristics:
Designed with a narrow and precise frequency response range, usually concentrated on the mid‑frequency human voice band (approximately 100Hz–6.8kHz), which is optimized for clear and natural voice transmission. The speaker features high sensitivity for easy driving with low power, ensuring stable volume and clear voice even when used with daily office equipment.
Call center headsets do not emphasize exaggerated bass or wide sound stage. All acoustic structures focus on reducing auditory fatigue during long‑term use and ensuring accurate, stable, and distortion‑free information transmission.
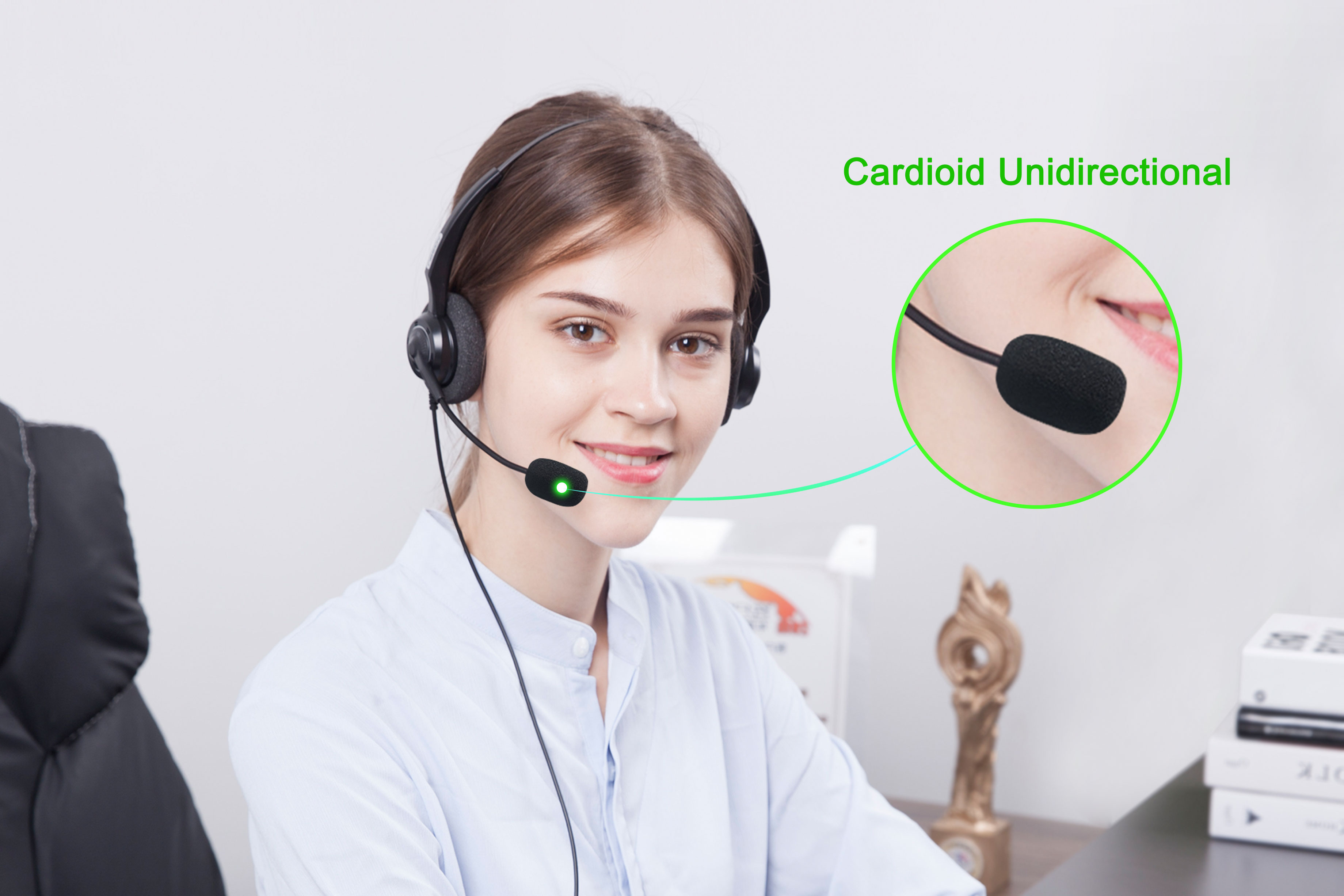
Key Supporting Component:
A high‑quality noise‑cancelling microphone (such as an electret microphone) is an indispensable configuration. It effectively suppresses background noise and ensures that customers can hear the agent’s voice clearly and stably.